Calican Parliament
| Calican Parliament Parlement calicien (French) Parlamento Calicano (Italian) Kaliski Parlament (Croatian) | |
|---|---|
|
20th Calican Parliament of the Calican Republic | |
| Type | |
| Type | Bicameral |
| Houses |
Senate Chamber of Deputies |
| Leadership | |
| President of the Senate |
Estelle Rodin, PL Since 12 April 2624 |
| President of the Chamber of Deputies |
Emiliano Curci, PL Since 12 April 2624 |
| President of the Calican Republic | Clément DuPont, PL |
| Structure | |
| Seats |
781 197 Senators 584 Deputies |
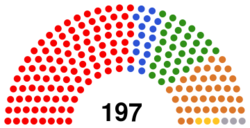 | |
| Senate political groups |
Liberal Party (104) Croatian Democratic Union (16) Forward Italy (33) Christian Conservative Party (38) Catalan National Party (3) Non inscrits (3) |
 | |
| Chamber of Deputies political groups |
Liberal Party (314) Croatian Democratic Union (43) Forward Italy (63) Christian Conservative Party (109) Catalan National Party (13) Green Party (24) Non inscrits (18) |
| Elections | |
| Senate voting system | Proportional representantion |
| Chamber of Deputies voting system | Single transferable vote |
| Senate last election | 12 April 2624 |
| Chamber of Deputies last election | 12 April 2624 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| [Palais de Caserte, Campanie] | |
The Calican Parliament is the bicameral legislature of the Calican Republic, consisting of the Senate (Sénat) and the Chamber of Deputies (Chambre des députés). Both houses conduct their sessions in separate buildings in the capital, meeting in the Palace of Caserte, Campanie for the opening of Parliament and for constitutional changes which require a vote of both houses together.
Contents
Organisation and Powers
The Parliament convenes for a single ten month session each year, excluding the months of December and July. Under exceptional circumstances, the President (Président) or Prime Minister (Premier ministre) can call an out of session convening of both houses of parliament. A government must retain the confidence of a majority of the Chamber of Deputies in order to operate effectively. The government must retain a majority in the lower house or form political alliances with other parties in order to retain majority power. With a vote of no confidence from a majority of the house, the government can be taken out of power, triggering a general election.
Cabinet
The Prime Minister is appointed by the President from the largest party in the Chamber of Deputies. In the situation that the political party of the President is different to the party of the Prime Minister, there is sometimes conflict in the government and promotes the parties to work together. The largest party in the lower house forms the government. The Cabinet of Ministers is selected by the President from either house of parliament. They are the leaders of the government ministries dealing with issues and the day to day running of government. The President can form a new Ministry (Ministère) of the government and appoint its leader at any point when the Parliament is in session. Parliament ministers do not require approval by parliament, as they are already Members of Parliament.
Opposition
The second largest party in the Senate forms the opposition party. The leader of the opposition party forms an opposition cabinet, mirroring all government ministers, in order to scrutinise the government and provide alternative viewpoints.
Presidents of the Houses
The Presidents of the houses act as the house speakers. The speakers of both houses are elected from their respective house by their own peers. When the leader is elected they must renounce all affiliation with their previous political party and remain strictly non-partisan. They do not vote in parliamentary votes apart from to break a tie. However, there are strict rules which dictate how the house president must vote in these situations. They must vote in favour of early readings of bills, against amendments to bills, against the final enactment of a bill and against motions of no confidence.
Composition
Senate
The Senate is composed of 197 elected members which are elected on the regional level. Each region is delegated a number of senators dependent on the population of the region.
| Region | Seats | Region | Seats | Region | Seats | Region | Seats | Region | Seats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abruzzes | 7 | Bosnie | 16 | Franche-Comté | 7 | Pouilles | 20 | Slovénie | 10 |
| Anticosti | 1 | Bourgogne | 8 | Herzégovine | 5 | Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur | 25 | Total | 197 |
| Atlantique | 1 | Calabre | 10 | Istrie | 5 | Rhône-Alpes | 35 | ||
| Auvergne | 7 | Campanie | 29 | Languedoc-Roussillon | 15 | Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon | 1 | ||
| Baléares | 7 | Corse | 3 | Malouines | 1 | Sardiagne | 8 | ||
| Basilicate | 7 | Croatie | 15 | Midi-Pyrénées | 16 | Sicile | 25 | ||
| Bermudes | 1 | Dalmatie | 7 | Molise | 11 | Slavonie | 7 |
Chamber of Deputies
Election
The election of the lower house uses instant-runoff voting to elect its members. The upper house, on the other hand, is elected dependent on the proportion of votes for a party in a region. For example, if a region had ten delegates and a party had 40% of the vote, they would get four seats in the Senate.
Election of the Senate
The 197 senators are elected on the regional level. Each region is delegated a number of senators dependent on the population of the region. Senators are elected using proportional representation in regions with more than one seat, where a first past the post system is used.
Election of the Chamber of Deputies
The Chamber of Deputies is composed of 584 deputies and is elected on a national level using instant-runoff voting which ranks each of the candidates on the ballot. Each deputy is elected to a constituency. Each department, the subdivision below a region, is split up into a number of geographical constituencies. The number of these constituencies per department is found so that around 65 000 population is represented by one seat in the lower house. With departments with less than 65 000 people, one seat is delegated. Currently, the département with the lowest population is Géorgie-du-Sud with only around 30 people.
Membership
Senate
The current membership of the Calican Senate, following the latest general election on 12 April 2624:
| Party | Leader | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liberal Party (PL) | Célia Garreau | 104 | |
| Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ) | Dejan Todorović | 16 | |
| Forward Italy (FI) | Pompeo Sacchetti | 33 | |
| Christian Conservative Party (PCC) | Luc Cailloux | 38 | |
| Catalan National Party (PNC) | Lluc Peña | 3 | |
| Non inscrits | N/A | 3 | |
| Total | 197 | ||
Chamber of Deputies
The current membership of the Calican Chamber of Deputies, following the latest general election on 12 April 2624:
| Party | Leader | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liberal Party (PL) | Célia Garreau | 314 | |
| Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ) | Dejan Todorović | 43 | |
| Forward Italy (FI) | Pompeo Sacchetti | 63 | |
| Christian Conservative Party (PCC) | Luc Cailloux | 109 | |
| Catalan National Party (PNC) | Lluc Peña | 13 | |
| Green Party (PV) | Marta Atlan | 24 | |
| Non inscrits | N/A | 18 | |
| Total | 584 | ||
