Nation/Vinland
| This page is a work in progress by its author(s) and should not be considered final. |
| Republic of Vinland and Markland Republik Vinland og Markland
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Motto: Af Guds nåde (By the grace of God) |
||||
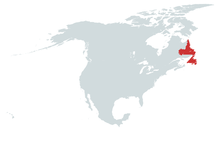
Location in North America
|
||||
Vinland
|
||||
| Capital and largest city | St. Jansted | |||
| Official languages | Danish | |||
| Recognised national languages | French, English | |||
| Recognised regional languages | Norwegian, Montagnais, Inuktitut (All in Markland) | |||
| Demonym | Vinlander (Vinlænder or Vinlænding) | |||
| Government | Unitary Constitutional Parliamentary Republic | |||
| - | President | Stephen Schou | ||
| - | Chancellor | Annie Knudsen | ||
| Legislature | Rigsdagen | |||
| Independence from Denmark | ||||
| - | English colony | 1610—1696 | ||
| - | Depopulation | November 1696 — April 1697 | ||
| - | Treaties of Utrecht (Acquisition by Denmark) | 1713 | ||
| - | Treaty of Kiel | January 14, 1814 | ||
| - | Kingdom | December 1, 1918 | ||
| - | Republic | June 17, 1944 | ||
| - | Reacquisition of Markland | July 1, 1962 | ||
| Area | ||||
| - | Total | 405,720 km2 156,649 sq mi |
||
| - | Water (%) | 7.7% | ||
| Population | ||||
| - | 2017 census | 528,817 | ||
| - | Density | 1.39/km2 3.6/sq mi |
||
| GDP (PPP) | 2011 estimate | |||
| - | Total | $26.304 billion | ||
| - | Per capita | $51,285.78 | ||
| Gini | 31.6 medium |
|||
| HDI | very high |
|||
| Currency | Vinlandic Krone (VKK) |
|||
| Time zone | (UTC−3.5 to −4) | |||
| - | Summer (DST) | (UTC−2.5 to −3) (UTC) | ||
| Date format | yyyy.mm.dd AD | |||
| Drives on the | right | |||
| Calling code | +1 | |||
| Patron saint | John the Baptist | |||
| Internet TLD | .vin | |||
Vinland (Danish pronunciation: [ˈviːˀnˌlanˀ]), officially the Republic of Vinland and Markland (Danish: Republik Vinland og Markland, [ʁεpuˈblig ˈviːˀnˌlanˀ ˈʌ ˈmɑːgˌlanˀ]) is a country located in the northeastern part of North America. It comprises the island of Vinland and mainland Markland to the northwest, with a combined area of 405,212 square kilometres (156,500 sq mi). About 92% of the nation's 528,817 residents live on the island of Vinland (and its neighbouring smaller islands), of which more than half reside on the Avalon Peninsula in the southeast corner of the island.
Vinland is a multinational state, comprising noteworthy populations of various ethnic and linguistic backgrounds. Just over 80% of residents report Danish as their mother tongue. Vinland is also home to a unique variety of French and was historically also home to a now-extinct variety of Irish as well. The extinct Beothuk language was at the time of European contact the primary language on the island of Vinland. In Markland, local dialects of Montagnais and Inuktitut are also spoken.
Vinland's capital and largest city, St. Jansted, is home to almost 40 percent of the nation's population. St. Jansted is the seat of government, home to the Rigsdag and to the highest court in the nation, the Højesteret.
Originally disputed by England and France in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, the territories Newfoundland and Labrador passed in possession to the crown of Denmark in 1713 following the Treaties of Utrecht as something of a pity-prize. The Danish government renamed the colonies to Vinland and Markland, in reference to the exploration of the land by Leif Erikson in the year 1000 AD. The territories were administered as a single colony until 1807, when Markland was split off from Vinland and placed under the authority of the Norwegian Government commission. As a result of this, Markland passed to Swedish rule in 1814 with Norway, while Vinland remained a Danish colony. In 1918, Vinland became an independent Kingdom of Vinland (1918—1944) within the Danish realm, which it remained until 1944 when the Monarchy was formally abolished and the nation became a republic. Markland remained a Norwegian possession until 1962, when it was transferred by Norway to Vinland as a result of the Nordic council's Helsinki Convention.